- Japan(Japanese / English)
- Global
- MBL TOP
- MBL site search

Types of Fluorescent Labels
| Fluorescence substances | |
|---|---|
| Fluorescent dyes (small molecular dyes) |
FITC (Fluorescein Isothiocyanate), Alexa Fluor® dyes, Cy dyes, etc. |
| Fluorescent proteins | PE (Phycoerythrin), APC (Allophycocyanin), etc. |
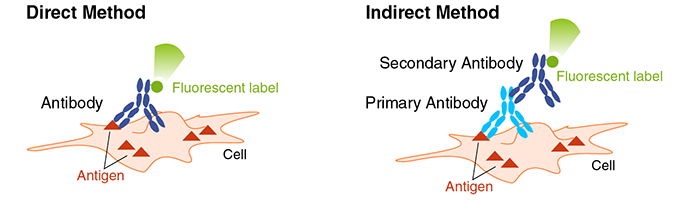
Direct Method vs. Indirect Method
There are two methods for detecting labeled antibodies: directly labeling the primary antibody with a fluorescent label (direct method), or using a fluorescently labeled secondary antibody that reacts with the primary antibody (indirect method). In direct method, multiple staining is easily achievable, but combinations of fluorescent dyes that do not interfere with each other needs to be considered.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
| Direct Method |
|
|
| Indirect Method |
|
|
Procedure for Fluorescent Immunostaining (Indirect Method)
※An example performed at MBL
↓ Cell seeding
↓ Cell fixation (using 4% paraformaldehyde, formalin, etc.)
↓ Washing
↓ Permeabilization (e.g. using surfactants)
↓ Washing
↓ Blocking
↓ Primary antibody reaction (at room temperature for 1-2 hours)
↓ Washing
↓ Fluorescent or enzyme-labeled secondary antibody reaction (at room temperature for 1 hour)
↓ Washing
↓ Counterstaining (e.g. with DAPI)
↓ Observation under a fluorescence microscope
Meaning of each step
▌ Cell fixation
To stabilize cell morphology and inactivate enzymes. The optimal fixation method depends on the antigen or antibody used, so the type of fixative, fixation time, and temperature should be considered for the best results.
| Aldehyde-based | Formaldehyde, paraformaldehyde, and formalin (aqueous solution of formaldehyde) are the most commonly used cross-linking agents. They react with the amino group (-NH2) of proteins and nucleic acids to form reversible bonds. Paraformaldehyde is sometimes prepared and used as a fixative. |
| Organic solvents | Organic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, and acetone can also be used as fixatives. In this case, lipids inside the cells are removed, so they cannot be used for detecting lipid-bound proteins such as membrane proteins. |
▌ Membrane permeabilization
To allow antibodies to penetrate the cell membrane and nuclear membrane after fixation. Surfactants like Triton X-100 or NP-40 are commonly used, and the concentration and duration of treatment should be adjusted based on the target protein.
▌ Blocking
To prevent non-specific staining by primary and secondary antibodies. Blocking agents like BSA or serum from the same host animal as the secondary antibody are used.
▌ Counterstaining
To visualize specific cellular structures by staining them with a color contrasting to the target protein. DAPI or Hoechst stains are commonly used to visualize the shape of the nucleus.
Items needed for experiment
• Cells to be stained (preferably adherent cells)
• Glass bottom dishes
• Substances to enhance cell adhesion (such as poly-L-lysine, collagen)
• Cell fixation solution (4% paraformaldehyde, formalin, methanol, etc.)
• Surfactants (NP-40, Triton X-100, Tween20, etc.)
• Blocking agents (BSA, serum, etc.)
• PBS
• 0.05-0.2% Tween20/PBS (PBS-T)
• Primary antibodies
• Fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies
• DAPI
• Water-soluble mounting medium
Method for Cell Culturing and Sample Preparation
※An in-house example of preparing cell samples using NRK cells will be introduced.
1. Cell culturing
 Cultivate NRK cells in a 10 cm dish. When cells reach approximately 70% confluency, collect and count the cells.
Cultivate NRK cells in a 10 cm dish. When cells reach approximately 70% confluency, collect and count the cells.
2. Cell seeding - (1)
Place an 18 mm x 18 mm coverslip autoclaved on a 6-well culture slide.
3. Cell seeding - (2)
Add 200 µL of the cell suspension adjusted to 5 x 105 cells/mL onto the coverslip(1 x 105/well).
Incubate for about 1 hour at 37°C in a 5%CO2 incubator.
4. Cell seeding - (3)
Add 2 mL of medium to each well and further incubate overnight.
5. Cell seeding - (4)
 ※If there is no need for specific treatment other than autophagy comparison, proceed to 6.cell fixation.
※If there is no need for specific treatment other than autophagy comparison, proceed to 6.cell fixation.
In the following day, remove the medium by aspiration after confirming cell adhesion under a microscope. Add 200 µL of 10% FCS-RPMI to the nutrient well and 200 µL of RPMI to the starved well. Incubate for about 3 hours at 37°C in a 5%CO2 incubator.
6. Cell fixation
Confirm cell adhesion under a microscope. Discard the medium, wash the cells with PBS, add 200 µL of 4% paraformaldehyde solution slowly, and let it stand at room temperature for 10 minutes.
7. Membrane permeabilization
Wash the cells twice with PBS, add 200 µL of 100 µg/mL digitonin in PBS to each well, and let it stand at room temperature for 10 minutes.
8. Primary antibody reaction
Wash the cells twice with PBS after removing the supernatant, add the primary antibodies diluted in PBS (200 µL each), and let it react at room temperature for 1 hour.
9. Fluorescent or enzyme-labeled secondary antibody reaction
Wash the cells three times with PBS, add the secondary antibodies diluted 500 times in PBS (200 µL each), cover with aluminum foil to block light, and let it react at room temperature for 30 minutes.
10. Counterstaining
Wash the cells three times with PBS, add DAPI (1 µg/mL, 100 µL), block light, and let it react at room temperature for 30 minutes.
11. Mounting
Wash the cells three times with PBS, mount them, and observe under a fluorescence microscope.