- Japan(Japanese / English)
- Global
- MBL TOP
- MBL site search
Close
This site is for customers in Japan.
Customers in other regions, please go to Global page.
HOME >
Product search results > Code No. D031-3
Anti-Proton Pump (H,K-ATPase α subunit) mAb
Price
¥48,000
Availability (in Japan)
10 or more
(In Japan at 17:33,
Apr 26, 2024 in JST)
Size
100 µL (1 mg/mL)
| Data | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clonality | Monoclonal | Clone | 1H9 | ||
| Isotype (Immunized Animal) | Mouse IgG1 | ||||
| Applications |
|
||||
| Reactivity [Gene ID] | |||||
| Storage buffer | PBS/50% glycerol, pH 7.2 | ||||
| Storage temp. | -20°C | Conjugate | Unlabeled | Manufacturer | MBL |
| Alternative names | ATP4A, ATP6A | ||||
| Background | Hydrogen-potassium adenosine triphosphatase (H+, K+-ATPase) belongs to a family of P-type cation-transporting ATPases that also includes Ca2+-ATPase and Na+, K+-ATPase. H+, K+-ATPase is responsible for acid secretion into the stomach and catalyzes electroneutral exchange of cytoplasmic hydrogen ions and external potassium ions coupled with ATP hydrolysis. The enzyme is found in gastric parietal cells where it is located in cytoplasmic vesicles or apical plasma membranes of the secretory canaliculus. H+, K+-ATPase is a heterodimer consisting of a high molecular weight catalytic a subunit and a smaller but heavily glycosylated b subunit. The a subunit of H+, K+-ATPase has 10 transmembrane domains and contains sites for ATP binding and its acylphosphorylation, binding sites of proton pump inhibitors, and sites responsible for ion recognition. | ||||
| Related products | D031-3H Anti-Proton Pump (H,K-ATPase α subunit) mAb D032-3 Anti-Proton Pump (H,K-ATPase β subunit) mAb D032-3H Anti-Proton Pump (H,K-ATPase β subunit) mAb |
||||
| Citations |
Western Blotting
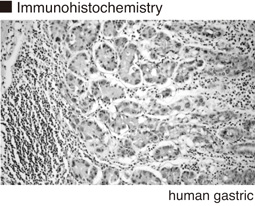
Immunohistochemistry
|
||||
| References |
|
||||
| Product category |
|
||||
- The availability is based on the information in Japan at 17:33, Apr 26, 2024 in JST.
- The special price is shown in red color.
- Please note that products cannot be ordered from this website. To purchase the items listed in this website, please contact us or local distributers.
- Abbreviations for applications:
WB: Western Blotting, IH: Immunohistochemistry, IC: Immunocytochemistry, IP: Immunoprecipitation
FCM: Flow Cytometry, NT: Neutralization, IF: Immunofluorescence, RIP: RNP Immunoprecipitation
ChIP: Chromatin Immunoprecipitation, CoIP: Co-Immunoprecipitation
DB: Dot Blotting, NB: Northern Blotting, RNA FISH: RNA Fluorescence in situ hybridization - For applications and reactivity:
*: The use is reported in a research article (Not tested by MBL). Please check the data sheet for detailed information.
**: The use is reported from the licenser (Under evaluation or not tested by MBL).
- For storage temparature: RT: room temparature
- Please note that products in this website might be changed or discontinued without notification in advance for quality improvement.









 Citations
Citations Data Sheet
Data Sheet