- Japan(Japanese / English)
- Global
- MBL TOP
- MBL site search
Close
This site is for customers in Japan.
Customers in other regions, please go to Global page.
HOME >
Product search results > Code No. K0220-3
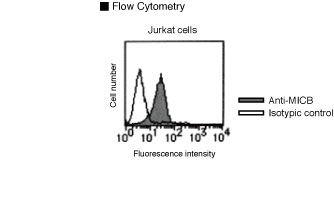
Anti-MICB (Human) mAb
Price
¥33,000
Availability (in Japan)
10 or more
(In Japan at 00:05,
Apr 24, 2024 in JST)
Size
100 µL (1 mg/mL)
| Data | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clonality | Monoclonal | Clone | BMO1 | ||
| Isotype (Immunized Animal) | Mouse IgG1 κ | ||||
| Applications | |||||
| Immunogen (Antigen) | MICA*01, MICA*04 and MICB*02 transfected P815 cells | ||||
| Reactivity [Gene ID] | Human[4277] |
||||
| Storage buffer | 1 mg/mL in PBS/50% glycerol, pH 7.2 | ||||
| Storage temp. | -20°C | Conjugate | Unlabeled | Manufacturer | MBL |
| Alternative names | MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence B, PERB11.2 | ||||
| Background | MICA and MICB (Major Histocompatibility Complex class I Chain-related gene A and gene B) bind to the activating immunoreceptor NKG2D. NKG2D is expressed on NK (Natural Killer) cells, NKT cells, γδT cells and CD8+ αβT cells. Recognition of MICA and MICB by NKG2D is involved in tumor surveillance, immune responses to viral infections and autoimmune diseases. MICA and MICB are transmembrane glycoproteins that are distantly related to the MIC proteins, and they possess three extra-cellular Ig-like domains. And thus, MICA and MICB are closely related but are functionally indistinguishable. MICA and MICB molecules are highly glycosylated, and are detected as a smear band ranging from 65-75 kDa. It is reported that MICA and MICB are highly expressed in variant tumor cells, whereas normal cells express little. Tumor cells have been shown to shed and release MIC molecules from the cell surface. Therefore determination of soluble MIC (sMIC) levels provides valuable information for cancer staging, and sMIC in serum seems to be an indicator for systemic manifestation of malignancy rather than for local tumor extent. | ||||
| Related products | K0217-3 Anti-MICA (Human) mAb K0218-3 Anti-MICA/B (Human) mAb K0219-3 Anti-MICA/B (Human) mAb |
||||
| Citations |
Flow Cytometry
|
||||
| Product category |
|
||||
- The availability is based on the information in Japan at 00:05, Apr 24, 2024 in JST.
- The special price is shown in red color.
- Please note that products cannot be ordered from this website. To purchase the items listed in this website, please contact us or local distributers.
- Abbreviations for applications:
WB: Western Blotting, IH: Immunohistochemistry, IC: Immunocytochemistry, IP: Immunoprecipitation
FCM: Flow Cytometry, NT: Neutralization, IF: Immunofluorescence, RIP: RNP Immunoprecipitation
ChIP: Chromatin Immunoprecipitation, CoIP: Co-Immunoprecipitation
DB: Dot Blotting, NB: Northern Blotting, RNA FISH: RNA Fluorescence in situ hybridization - For applications and reactivity:
*: The use is reported in a research article (Not tested by MBL). Please check the data sheet for detailed information.
**: The use is reported from the licenser (Under evaluation or not tested by MBL).
- For storage temparature: RT: room temparature
- Please note that products in this website might be changed or discontinued without notification in advance for quality improvement.








 Citations
Citations Data Sheet
Data Sheet