Antibody detailed product information
| Code No. | MD-10-4 | |
| Anti-Fas (CD95) (Human) mAb-FITC | ||
| Size | 100 µL (500 µg/mL) | |
| Availability (in Japan) | 10 or more
(In Japan at 17:00, Apr 16, 2024 in JST) |
|
| Clonality | Monoclonal | |
| Clone | UB2 | |
| Isotype (Immunized Animal) |
Mouse IgG1 | |
| Applications | FCM 10 µg/mL |
|
| Immunogen (Antigen) |
Recombinant Human Fas | |
| Reactivity [Gene ID] | Human[355], Mouse(-) |
|
| Storage buffer | 500 µg/mL in PBS/1% BSA/0.1% ProClin 150 | |
| Storage temp. | 4°C | |
| Conjugate | FITC | |
| Manufacturer | MBL | |
| Alternative names | APT1, FAS1, APO-1, FASTM, ALPS1A, TNFRSF6 | |
| Background | It is now widely accepted that apoptosis plays an important role in the selection of immature thymocytes and Ag-primed peripheral T cells. Fas antigen is a cell-surface protein that mediates apoptosis. It is expressed in various tissues including the thymus and has structural homology with a number of cell-surface receptors, including tumor necrosis factor receptor and nerve growth factor receptor. | |
| Related products | SY-001 Anti-Fas (CD95) (Human) mAb MD-10-3 Anti-Fas (CD95) (Human) mAb MD-10-5 Anti-Fas (CD95) (Human) mAb-PE MD-10-A48 Anti-Fas (CD95) (Human) mAb-Alexa Fluor™ 488 MD-11-3 Anti-Fas (CD95) (Human) mAb M075-4 Mouse IgG1 (isotype control)-FITC |
|
| Product category | Research area:Apoptosis Cell surface antigens | |
| Data | 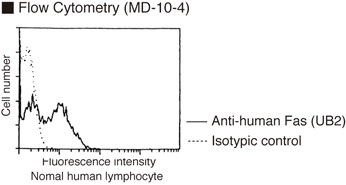 |
|
| Citations | Flow Cytometry
|
|
- The availability is based on the information in Japan at 17:00, Apr 16, 2024 in JST.
- The special price is shown in red color.
- Please note that products cannot be ordered from this website. To purchase the items listed in this website, please contact us or local distributers.
- Abbreviations for applications:
WB: Western Blotting, IH: Immunohistochemistry, IC: Immunocytochemistry, IP: Immunoprecipitation
FCM: Flow Cytometry, NT: Neutralization, IF: Immunofluorescence, RIP: RNP Immunoprecipitation
ChIP: Chromatin Immunoprecipitation, CoIP: Co-Immunoprecipitation
DB: Dot Blotting, NB: Northern Blotting, RNA FISH: RNA Fluorescence in situ hybridization - For applications and reactivity:
*: The use is reported in a research article (Not tested by MBL). Please check the data sheet for detailed information.
**: The use is reported from the licenser (Under evaluation or not tested by MBL).
- For storage temparature: RT: room temparature
- Please note that products in this website might be changed or discontinued without notification in advance for quality improvement.
 Copyright (C)2015 Medical & Biological Laboratories Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserve
Copyright (C)2015 Medical & Biological Laboratories Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserve