- Japan(Japanese / English)
- Global
- MBL TOP
- MBL site search
Phospho-p62
Hot topic in research on neurodegenerative disease and cancer
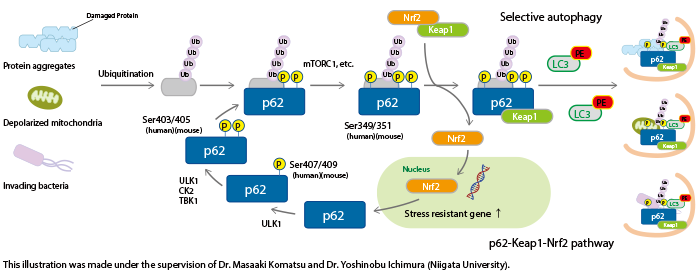
p62 contains multiple phosphorylation sites. Sequential phosphorylation of these sites regulates biological defense mechanisms such as selective autophagy.
The phosphorylation of Ser407 (human)/Ser409 (mouse) precedes the phosphorylation of Ser403 (human)/Ser405 (mouse) in p62, which increases its affinity for poly ubiquitin chains. Consequently, ubiquitinated abnormal protein aggregates, depolarized mitochondria, and invading intracellular bacteria are sequestered by phospho-p62. Further phosphorylation of Ser349 (human)/Ser351 (mouse) by mTORC1 increases the affinity of p62 for Keap1, inducing dissociation of Nrf2 from Keap1 and nuclear translocation of Nrf2 (the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 pathway). Nrf2 is a
stress-response transcription factor and activates the transcription of various stress resistance genes. Nrf2 also induces p62 gene expression, forming a positive feedback loop. Phospho-p62 with bound Keap1 interacts with LC3 through the LIR (LC3-interacting region) and is degraded by the autophagy pathway. Thus, the cells under stress conditions effectively overcome their negative environment by activating two biological defense mechanisms through the phosphorylation of p62.
Impaired selective autophagy is implicated in various diseases. For example, neurons in familial parkinsonism fail to clear protein aggregates and depolarized mitochondria, resulting in neuronal damage and compromised brain function. In hepatocarcinoma cells, p62 is constitutively phosphorylated at Ser349, causing continuous activation of Nrf2. Hence, inhibitors of p62 phosphorylation and inhibitors of the interaction between phospho-p62 and Keap1 have the potential to be novel cancer therapeutics.
(Reference: Saito, T., et al., Nat. Commun. 7, 12030 (2016) PMID: 27345495).
■ The p62-Keap1-Nrf2 pathway




 p62 and phospho-p62 ELISA Kit
p62 and phospho-p62 ELISA Kit